40 label the structures of the thoracic cavity.
What is the role of thoracic spinal nerve blocks in pain ... - Medscape Answer. Thoracic paravertebral somatic or selective blocks (SNRBs) can alleviate pain involving the thoracic paraspinal regions, chest, and abdomen. SNRBs are helpful in determining the cause of ... › worksheets › rat_dissectionRat Dissection Step 7 - The Biology Corner These organs are large bean shaped structures located toward the back of the abdominal cavity on either side of the spine. Renal arteries and veins supply the kidneys with blood. 2. Locate the delicate ureters that attach to the kidney and lead to the bladder. Wiggle the kidneys to help locate these tiny tubes.
Serous Membranes of the Abdominal Cavity - MHMedical.com Parietal peritoneum. The portion of the serous sac in contact with the internal surface of the abdominal wall, diaphragm, and pelvis. The posterior surface of the parietal peritoneum forms the anterior wall of the retroperitoneal space, which contains the kidneys, ureters, adrenal glands, aorta, IVC, and other structures. Visceral peritoneum.
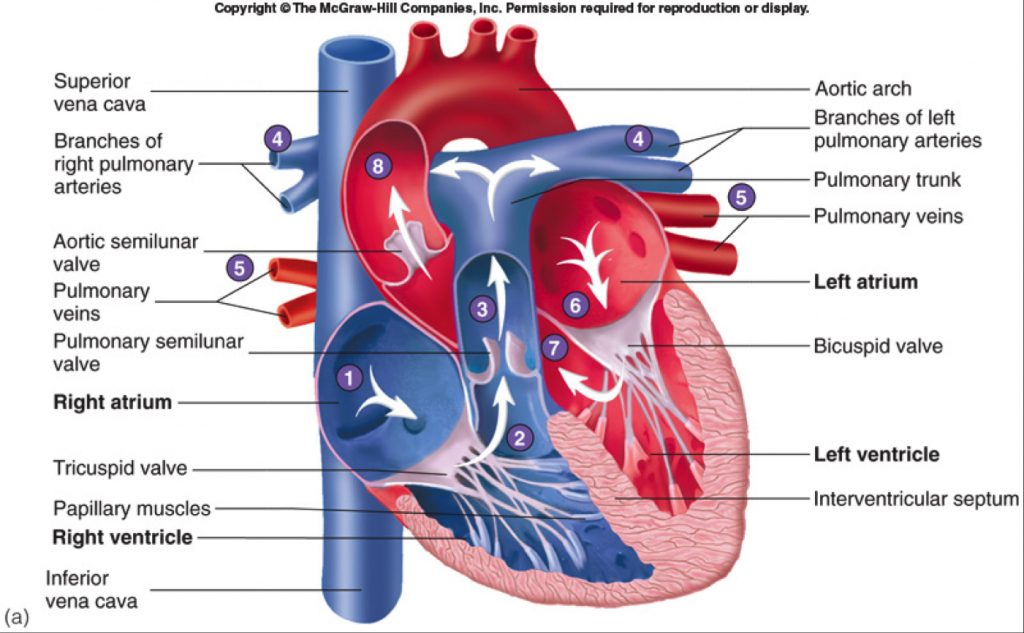
Label the structures of the thoracic cavity.
Creating Model Working Lungs: Just Breathe - Activity The artificial lung is approximately 18-inches long and consists of membranes that pass oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide. It is inserted through a vein in the leg and lodged in the main vein (the vena cava) passing blood to the heart. The blood is re-oxygenated through a catheter attached to an oxygen supply. Trunk Region (Torso) < Regional Anatomy << Human Anatomy <<< Body ... In our body's torso, the Internal Structures of our thorax region (chest) include the diaphragm, esophagus, trachea and xiphoid process (metasternum) . External Structures of our Thorax Region (Chest) In our body, the External Structures of our Thorax Region (Chest) include the Breast, Nipples and Mammary Glands. [2726] "Mammary Region (Breasts)" Blunt Chest Trauma - What You Need to Know - Drugs.com Blunt chest trauma is a sudden, forceful injury to your chest. It is often caused by a car or motorcycle accident, blast injury, or a fall. It may also be caused by a sports injury, such as a hit from a baseball. You may have no signs or symptoms, or you may have bruising, pain, or soreness.
Label the structures of the thoracic cavity.. Chapter 8. Serous Membranes of the Abdominal Cavity The peritoneum is a serous membrane that consists of two layers: parietal peritoneum and visceral peritoneum ( Figure 8-1A-C ). The parietal peritoneum lines the internal walls of the abdominal cavity, forming a closed sac known as the peritoneal cavity. The peritoneal cavity is completely closed in males. apps.who.int › classifications › icd10ICD-10 Version:2016 - WHO Quick Search Help. Quick search helps you quickly navigate to a particular category. It searches only titles, inclusions and the index and it works by starting to search as you type and provide you options in a dynamic dropdown list. Co-registration of mouse cortical structures between in vivo and ex ... Label the neuronal structure with calcium indicator (GCaMP, Figure 1 A). ... Under isoflurane (initial: 5%, maintain: 3%) anesthesia, expose thoracic cavity. 5. Insert the blunt perfusion needle ... Thoracic Disc Herniation - What You Need to Know - Drugs.com Thoracic disc herniation occurs when a thoracic disc bulges out from between your vertebrae. Discs are spongy cushions between the vertebrae in your spine. Thoracic discs are located between the base of your neck and your lower back. The herniated disc may press on your nerves or spinal cord.
teachmeanatomy.infoTeachMeAnatomy - Making Anatomy Simple Containing over 700 vibrant, full-colour images, TeachMeAnatomy is a comprehensive anatomy encyclopedia presented in a visually-appealing, easy-to-read format. Muscles of Respiration and How They Work | New Health Advisor It is a complex arrangement of all the muscles which are attached to the rib cage, and help in generating the breathing action. These muscles include inspiratory muscles which cause the thoracic cavity to expand or induce inhalation and expiratory muscles which compress the thoracic cavity or induce exhalation. Pleural Cavity: Anatomy, Effusion Causes, Treatment The pleural cavity is the area that lies between the parietal pleura (outer layer), that is attached to the chest wall and the visceral pleura (inner layer) that is attached to the lungs. 1 Within the pleural space is between 15 and 20 ccs of fluid (roughly three to four teaspoons) secreted by cells in the pleura. Multiple choice paper on anatomy - USA Elite Writers Label each of the following statements with a (D) if it applies to the dorsal body cavity or a (V) if it applies to the ventral body cavity. (5 pts) 1. Includes the thoracic cavity. 2. Includes the abdominopelvic cavity. 3. Holds the brain and spinal chord. 4.Holds the heart, lungs, and digestive organs. 5.
BIOLOGY FORM TWO SUMMARIZED NOTES - Educationnewshub.co.ke Demonstrate the breathing mechanism of the lungs and diaphragm in a model thoracic cavity Demonstrate the breathing movement of ribs and muscles by using a model Examine the factors affecting the rate of breathing in human beings Explain the factors which control the rate of breathing in human beings State the causes of respiratory diseases Multiple choice paper on anatomy - Assignment Worker Label each of the following statements with a (D) if it applies to the dorsal body cavity or a (V) if it applies to the ventral body cavity. (5 pts) 1. Includes the thoracic cavity. 2. Includes the abdominopelvic cavity. 3. Holds the brain and spinal chord. 4.Holds the heart, lungs, and digestive organs. 5. Sectioning and Counting of Motor Neurons in the L3 to L6 Region of the ... 4. Using scissors trim off all skin, arms, legs, ribcage, and contents of thoracic and abdominal cavity in order to isolate the spinal column (Fig. 1C). Trim spinal column tight to the vertebrae on either side down past the pelvic girdle. This shortens the length of the spinal nerves which would otherwise impair the flush process. 5. Which histologic findings are characteristic of esophageal ... - Medscape References. Answer. Histologically, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is characterized microscopically by keratinocyte-like cells with intercellular bridges or keratinization. Adenocarcinomas ...
Toxicological responses to sublethal anticoagulant rodenticide exposure ... An important component of assessing the hazards of anticoagulant rodenticides to non-target wildlife is observations in exposed free-ranging individuals. The objective of this study was to determine whether environmentally realistic, sublethal first-generation anticoagulant rodenticide (FGAR) exposures via prey can result in direct or indirect adverse effects to free-flying raptors. We offered ...
Respiratory System Organs and Their Functions - New Health Advisor The airways (nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx etc.) allow air to enter the body and into the lungs. The lungs work to pass oxygen into the body, whilst removing carbon dioxide from the body. The muscles of respiration, such as the diaphragm, work in unison to pump air into and out of the lungs whilst breathing. Physiology of Gas Exchange
Circulatory system - Wikipedia The circulatory system includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The cardiovascular system in all vertebrates, consists of the heart and blood vessels. The circulatory system is further divided into two major circuits - a pulmonary circulation, and a systemic circulation. The pulmonary circulation is a circuit loop from the right heart taking deoxygenated blood to the lungs where it is ...
EOF
open.oregonstate.education › aandp › chapter20.2 Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, and Resistance – Anatomy ... This in turn promotes the return of blood from the thoracic veins to the atria. During exhalation, when air pressure increases within the thoracic cavity, pressure in the thoracic veins increases, speeding blood flow into the heart while valves in the veins prevent blood from flowing backward from the thoracic and abdominal veins.
Mechanism of Respiration in Human Beings - Embibe These actions increase the volume of the thoracic (chest) cavity, and the air (oxygen) is forced into the lungs. On the contrary, exhalation occurs when the thoracic cavity is reduced, and the air (carbon dioxide) is expelled out. Practice Exam Questions Fig: Mechanism of Breathing 2.
Blunt Chest Trauma - What You Need to Know - Drugs.com Blunt chest trauma is a sudden, forceful injury to your chest. It is often caused by a car or motorcycle accident, blast injury, or a fall. It may also be caused by a sports injury, such as a hit from a baseball. You may have no signs or symptoms, or you may have bruising, pain, or soreness.
Trunk Region (Torso) < Regional Anatomy << Human Anatomy <<< Body ... In our body's torso, the Internal Structures of our thorax region (chest) include the diaphragm, esophagus, trachea and xiphoid process (metasternum) . External Structures of our Thorax Region (Chest) In our body, the External Structures of our Thorax Region (Chest) include the Breast, Nipples and Mammary Glands. [2726] "Mammary Region (Breasts)"
Creating Model Working Lungs: Just Breathe - Activity The artificial lung is approximately 18-inches long and consists of membranes that pass oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide. It is inserted through a vein in the leg and lodged in the main vein (the vena cava) passing blood to the heart. The blood is re-oxygenated through a catheter attached to an oxygen supply.



Post a Comment for "40 label the structures of the thoracic cavity."